M270 Waste Management: An Innovative Solution for Managing Harmful Waste
M270 Waste Management: An Innovative Solution for Managing Harmful Waste
Blog Article
Innovative PFAS Therapy Solutions for Safer Water
The enhancing frequency of PFAS contamination in water materials demands an important assessment of innovative therapy solutions. Advanced filtering technologies and novel chemical therapies present appealing methods for decreasing these persistent toxins. Additionally, emerging bioremediation strategies supply a more lasting strategy to tackling PFAS difficulties. As governing structures continue to adapt, comprehending the performance and scalability of these solutions ends up being extremely important. What implications do these improvements hold for public wellness and ecological reconstruction, and just how can stakeholders effectively implement them in varied contexts?
Review of PFAS Contamination
PFAS contamination has actually become a significant ecological and public health issue. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl compounds (PFAS) are a group of synthetic chemicals known for their determination in the atmosphere and human body, leading them to be typically referred to as "permanently chemicals." These substances have been commonly used in various industries, consisting of firefighting foams, water-repellent textiles, and food product packaging, primarily due to their water- and grease-resistant buildings.
The prevalent use PFAS has resulted in their detection in dirt, water materials, and even in the blood of humans and animals. Researches have linked PFAS direct exposure to countless health and wellness problems, including developing impacts in babies, immune system dysfunction, and numerous types of cancer. In addition, the ecological determination of these compounds complicates their destruction and removal, raising problems regarding long-term eco-friendly effects.
Regulatory bodies are significantly carrying out stringent standards to keep track of and decrease PFAS degrees in alcohol consumption water and various other environmental mediums. As awareness of PFAS contamination expands, it has ended up being essential for areas and markets to look for effective therapy services to minimize exposure and guard public health and wellness.
Advanced Purification Technologies
As the seriousness to address PFAS contamination increases, advanced filtering technologies have arised as a critical part in the removal efforts intended at removing these consistent chemicals from water resources. These technologies take advantage of innovative mechanisms to efficiently target and record PFAS compounds, which are notoriously immune to traditional therapy approaches.
One of the most encouraging approaches is using granular triggered carbon (GAC), which adsorbs PFAS particles because of its high area and permeable structure. This approach has actually been extensively carried out in both local and commercial settings, showing significant reductions in PFAS concentrations. Additionally, ion exchange materials have actually gained traction, particularly created to uniquely bind PFAS ions from water, hence facilitating their elimination.
Membrane layer filtering technologies, such as reverse osmosis and nanofiltration, also reveal efficiency in PFAS removal by physically dividing contaminants from water - pfas management. These systems can achieve high levels of purity, making article them appropriate for drinking water applications
Chemical Treatment Developments
Many chemical treatment developments are being checked out to successfully attend to PFAS contamination in water materials. One appealing technique includes making use of sophisticated oxidation processes (AOPs), which utilize effective oxidants such as ozone, hydrogen peroxide, or chlorine dioxide incorporated with UV light to damage down PFAS compounds into less harmful materials. This approach has actually demonstrated efficacy in research laboratory setups, revealing potential for scalability in real-world applications.
Another innovative strategy is the growth of ion-exchange materials particularly designed to target PFAS. These materials can precisely adsorb PFAS compounds from water, permitting their elimination during treatment procedures. Current advancements have actually enhanced the efficiency and ability of these resins, making them a beneficial option for water therapy centers.
Furthermore, researchers are exploring making use of chemical agents like persulfate and ferrous ions to boost the degradation of PFAS in infected water. These agents can generate chemical responses that help with the breakdown of consistent PFAS compounds.
Arising Bioremediation Techniques
Current advancements in chemical therapy innovations have actually led the way for checking out bioremediation methods as a viable option for dealing with PFAS contamination. Bioremediation uses the natural metabolic procedures of microorganisms to break down or change pollutants, making it an attractive strategy for dealing with relentless contaminants like PFAS.
Arising strategies in bioremediation include using genetically crafted microbes that can specifically target and damage down PFAS substances. These microbial stress are being established for their boosted degradation abilities, boosting the efficiency of the remediation process. Furthermore, scientists are investigating the possibility of plant-assisted bioremediation, explanation where specific plant varieties may uptake and sequester PFAS from polluted dirt and water.
An additional encouraging approach is the application of bioaugmentation, which involves presenting useful bacteria into infected environments to enhance the deterioration of PFAS. This technique can facilitate much faster removal timelines and improve total performance.
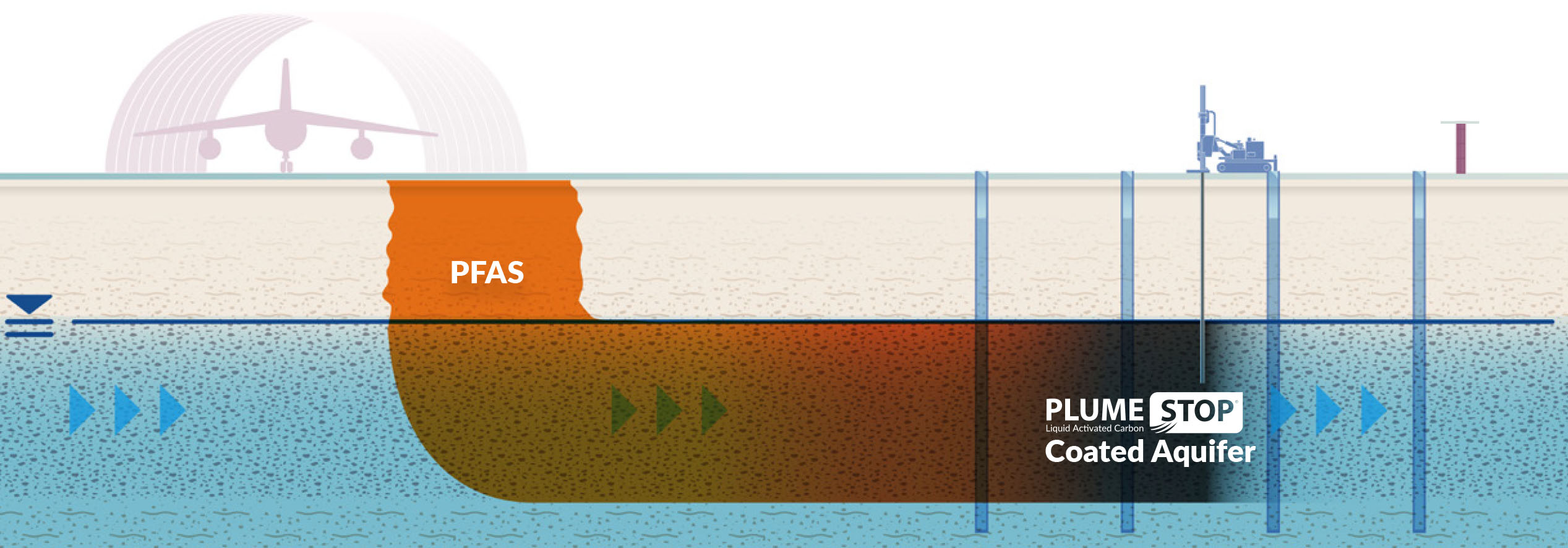
Regulative Structures and Requirements
A thorough regulatory structure is essential for effectively managing PFAS contamination and guaranteeing public health protection. The enhancing acknowledgment of per- and polyfluoroalkyl materials (PFAS) as ecological contaminants has prompted various federal and state firms to create criteria that regulate their existence in water materials. The United State Environmental Defense Firm (EPA) has actually established health advisories and is pursuing establishing enforceable limitations for PFAS in drinking water.
State-level regulations differ dramatically, with some states embracing stricter guidelines than those recommended by the EPA. These guidelines typically include optimum impurity levels (MCLs) for specific PFAS substances, tracking needs, and reporting responsibilities for water energies. Additionally, emerging structures concentrate on the removal of polluted sites, stressing the requirement for efficient therapy modern technologies.

Final Thought
In final thought, the development and execution of cutting-edge PFAS treatment solutions are essential for attending to the pervasive concern of water contamination. Advanced purification innovations, chemical treatments, and arising bioremediation techniques jointly provide a find this multifaceted strategy to successfully decrease and weaken PFAS levels. As governing frameworks continue to progress, integrating these modern technologies will be important to secure public health and recover the integrity of infected water sources, ultimately contributing to a cleaner and more secure environment.
Report this page